Context: Modern Digital Transformation
Optimization, Automation
Video
Assess
Chat
AI, Insights
Video
Assess
Chat
Returns / Capital
Video
Assess
Chat
Max. Capabilities
Video
Assess
Chat
Cost: High --- Value: Low
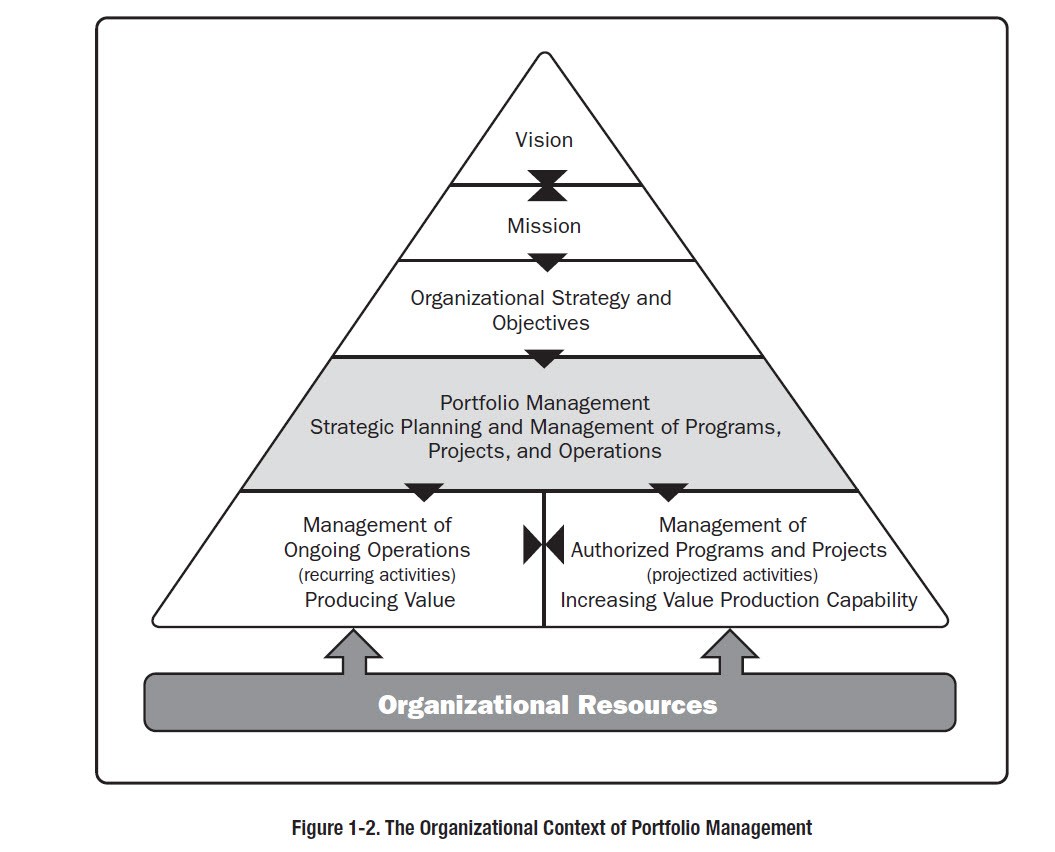
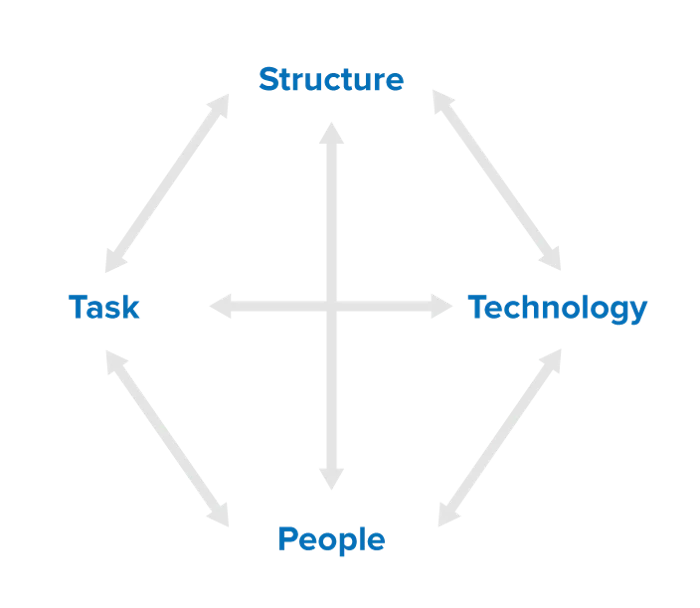
The core set up of the organization. Mission, vision, current strategy. Roles and responsibilities should align with the strategy.
Video
Assess
Chat
Why is the operating model value low?
Natural hierarchy is static. In a human family or collective the actors may change, but the chain of command does not. Contrary to this, the model of organizations evolves given market conditions, disruptions, and internal factors. Therefore, executing changes to the operating model is costly because the everyone in the chain of command needs to respect these changes as a collective, while the value of those changes to the hierarchy is minimal or intangible.
Cost: High --- Value: High
Expertise within the organization. It aggregates skills, intellectual property, and the potential for innovation.
Video
Assess
Chat
Why is the capabilities cost high?
Because human resources are the highest cost factor, the cost increases with the size of the operating model. This also means that the capabilities increase, and that strategies can be more refined and more initiatives can be executed.
On the other hand, tasks, processes, and procedures that rely on minimal decisive intelligence should be automated, outsourced, or eliminated.
Cost: Low --- Value: Low
The execution of operations and strategy. Operational and strategic process groups should be optimized and automated.
Video
Assess
Chat
Why is the process value low?
Processes and procedures are overhead due to the lack of trust in the individuals ability to execute to quality. The more individuals take part in any given process, the longer it takes to get the given output. Highly skilled resources are restricted by process (i.e. R&D) while standardized processes enforce the same quality of output. If all resources were highly skilled, fit for the tasks given as well as living intrinsic work ethics and values, processes would be superfluous.
Cost: Low --- Value: High
Integrates information for all roles in the organization. Generated reports should depict the current state as close as possible.
Video
Assess
Chat
Why is the insights value high?
Processes and procedures are overhead due to the lack of trust in the individuals ability to execute to quality. The more individuals take part in any given process, the longer it takes to get the given output. Highly skilled resources are restricted by process (i.e. R&D) while standardized processes enforce the same quality of output. If all resources were highly skilled, fit for the tasks given as well as living intrinsic work ethics and values, processes would be superfluous.
Cost-Value Flows
Strategy Flow
Operations Flow
Execution Flow
Innovation Flow
Strategy and Operation Alignment Examples
The choice will depend on company culture and budgetary constraints.
Other capabilities are any assets that help deliver the strategy, including intellectual property and physical assets (as defined by accounting).
The cost-value matrix states that:
The predicted success of strategy is the sum of the desired capabilities.
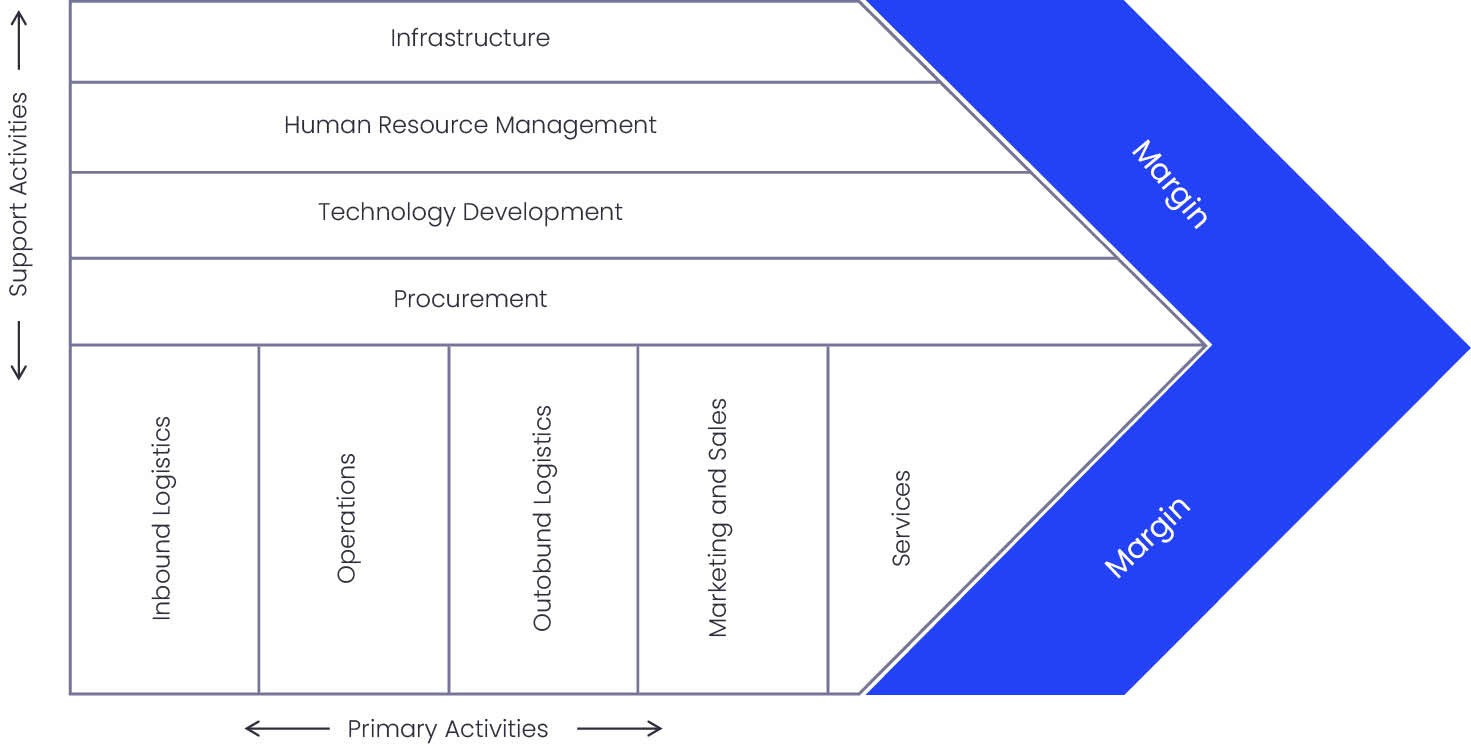
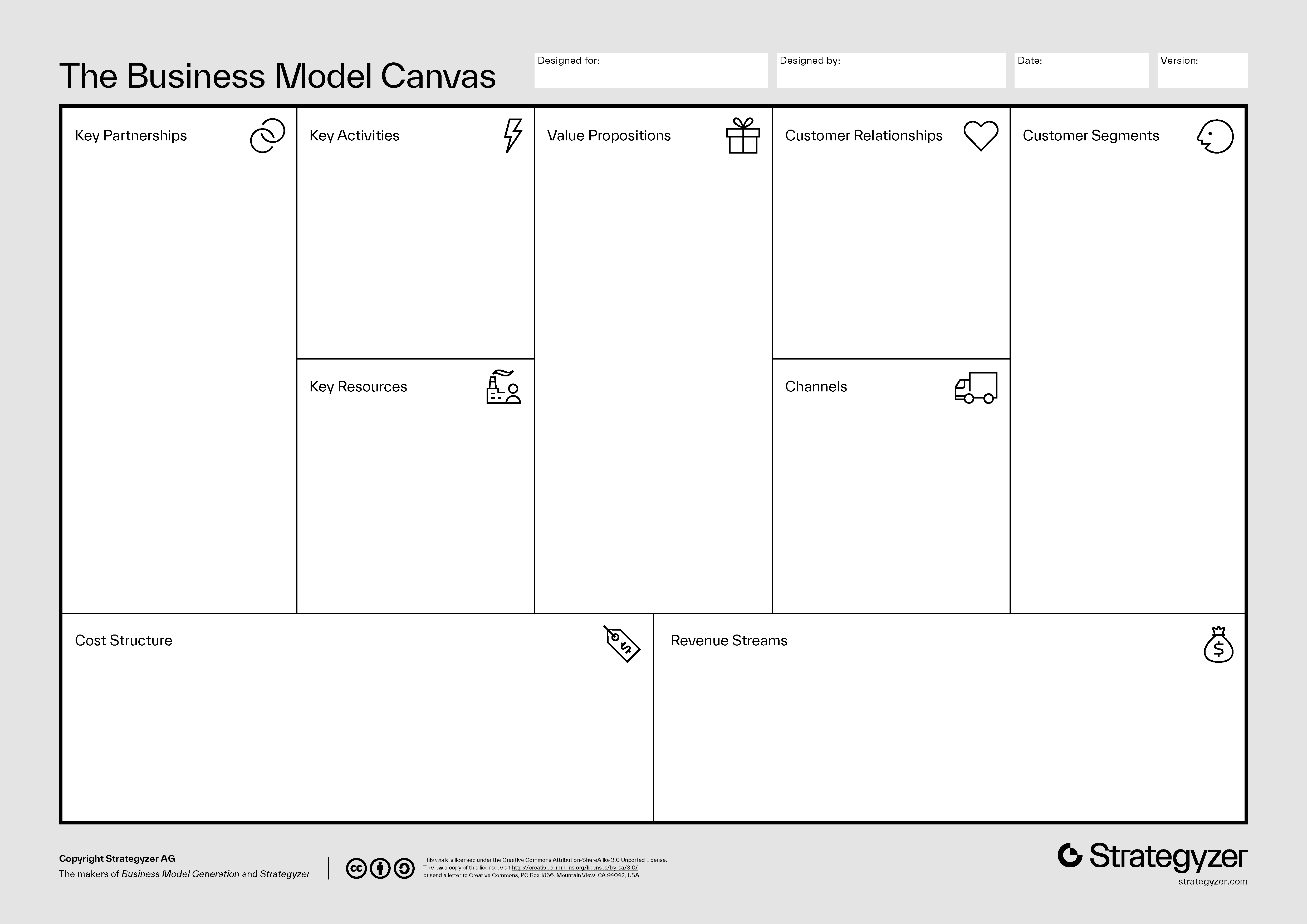
Each element in the Business Model Canvas can be viewed as structured, data-based interactions. For example, Cost Structure and Revenue Streams are following Accounting processes; Key Activities are generating the Process Outcomes; Key Resources need to be managed (onboarded, offboarded, incentivized, controlled); and Customer Relations, Channels, and Customer Segments are equal to Marketing and Sales processes.
Service-centric organizations are quicker to adjust each element and thus, have to be more careful to avoid reducing the quality of service when modifying processes.
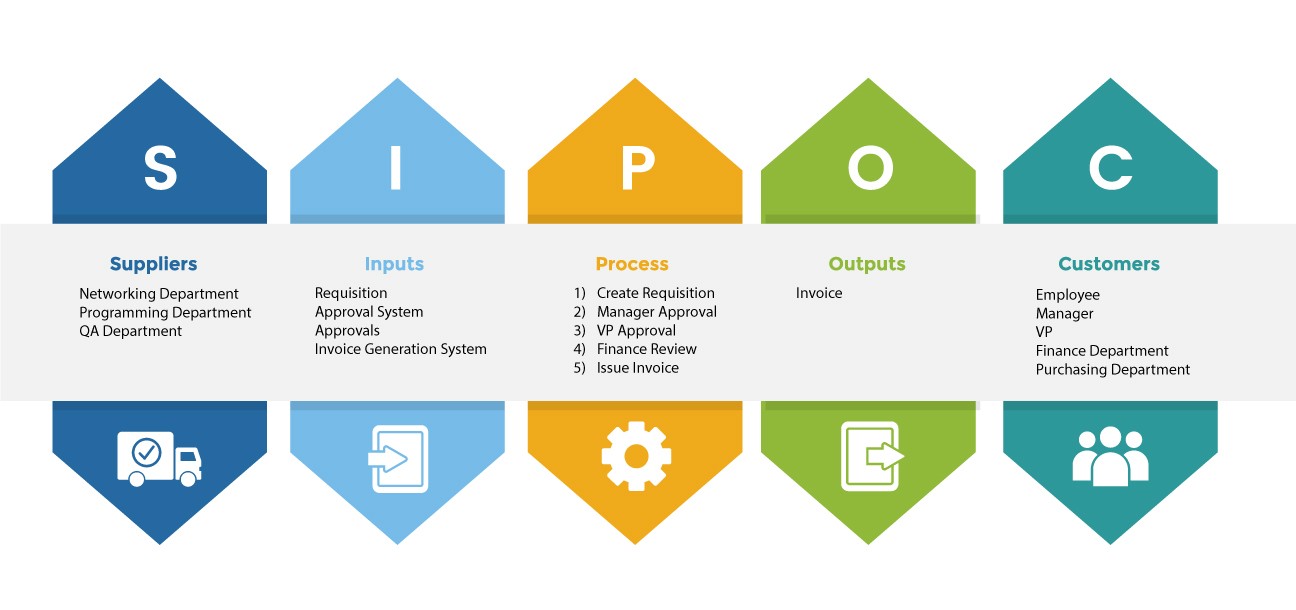
To complete the picture of processes, each process requires tools and often templates to work with, be it either in a manufacturing plant, hospital, branch of a bank, or back office at Headquarters. Getting a complete picture of a process through the SIPOC method can reveal
Outdated assumptions;
Use of unnecessary tools
Overengineering; or
Lack of integration with other, newer processes in the same process group.
See a sample SIPOC process for invoicing below:
When processes are contained within the organization, it is unnecessary to list Suppliers and Customers as they will be the same. For those processes, one can only define Inputs, Process, and Outputs.
The cost-value matrix states that:
The executed success of strategy is the sum of value of all processes.
The quickest win to amend value to an organization is transparent reporting.
Organizational culture, security clearance requirements, and use of legacy systems can hinder advancing such reporting efforts. Furthermore, security structures can be difficult to model in BI tools and the use of AI is prohibitive on Personal Identifiable Information (PII), thus, making it more difficult to implement 360 reporting views.
To conquer these challenges, the organization can centralize the distribution of information by establishing a Community for Insights or an Analytics Center of Excellence.
For example, Microsoft published a blueprint for a Reporting Center of Excellence and provides guidance on how to establish one in any organization.
Further enhancing reporting with Machine Learning Models allows for AI to be introduced safely to the organization, given that processes and data are security trimmed and PII is handled appropriately. For example, contact information of sales lead should only be accessible by users and groups that would be allowed to contact them.
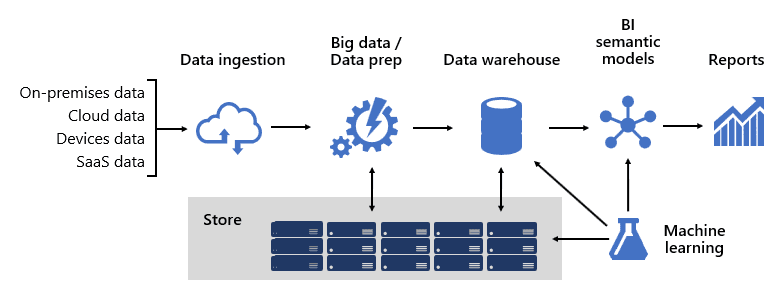
Investigating the data pipeline helps determine responsibilities and security for data across the organization. The following diagram shows the Microsoft Azure BI platform:
The data sources and security groups and considerations are paramount to build and continuously improve an Analytics Center of Excellence.
Th quality of outputs from Machine Learning Models is highly dependent on the quality of the data used. It is not uncommon to iterate multiple years over versions of the same model before deploying successfully to a broader, internal audience.
The low-hanging fruit is the creation of the reports. Given that a robust BI platform exists, procuring or training the capabilities to create those valuable insights should be accomplished in the short-term.
The cost-value matrix states that:
All levels of the operating model have access to the predicted and executed success of strategy.
Assessing the operating model, capabilities, processes, and reporting brings organizations closer to realize the vision. The objective is to reveal opportunities to automate, optimize, and innovate. The result should be a list of prioritized gaps that need to be closed to get closer to the vision with value propositions for each initiative.
If any metric can not be tracked across each element, we assume a disconnect between strategy and execution.
Eventually, the cost-value matrix is a tool that allows anyone in the organization to discover opportunities for improvement and innovation. The most efficient application of the cost-value matrix will start as a top-down approach to guarantee the most complete information on the four elements.
References
1) Project Management Institute. The Standard for Portfolio Management. 3rd ed., Project Management Institute, 2013.
2) Korukonda, R. Korukula. Organizational Portfolio Management: A Practitioner’s Guide. J. Ross Publishing, 2013.
3) Osterwalder, Alexander, and Yves Pigneur. Business Model Generation: A Handbook for Visionaries, Game Changers, and Challengers. Wiley, 2010.
4) Osterwalder, Alexander, et al. The Invincible Company: How to Constantly Reinvent Your Organization with Inspiration from the World's Best Business Models. Wiley, 2020.
5) Leavitt, Harold J. "Applied Organizational Change in Industry: Structural, Technological, and Humanistic Approaches." New Perspectives in Organizational Research, edited by Warren G. Bennis, Kenneth D. Benne, and Robert Chin, Wiley, 1969, pp. 55-71.
6) Porter, Michael E. Competitive Advantage: Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance. Free Press, 1985.
7) "Center of Excellence - Business Intelligence Solution Architecture." Microsoft Learn, Microsoft. Accessed 2 July 2024., Weblink.